Dedicated to making a difference in people's lives
Today, over 50 million people are living with dementia, Parkinson’s disease affects over 6 million people worldwide and neurological orphan, or NeuroOrphan, diseases, collectively affect more than 8 million people in the U.S alone. Our goal is to develop treatments and preventive strategies that will make a difference in the lives of patients, their families and caregivers.
AC Immune is pioneering precision medicine for neurodegenerative diseases and advancing a broad portfolio of active immunotherapies, antibodies and small molecules to allow tailoring of the best combination of modalities to each patient’s diagnostic profile. Our diagnostic candidates promise to empower reliable and refined diagnosis based on well-defined biomarkers.
This approach is enabled by our clinically validated technology platforms, SupraAntigen® and Morphomer®, which generate sensitive diagnostics, highly specific biologics and small molecule drugs. The drug candidates are selected to distinguish normal from pathological proteins and inhibit key disease pathways both inside and outside of cells. We believe that, beyond targeted monotherapies, combination therapy will offer greater efficacy in treating the broad spectrum of pathologies.
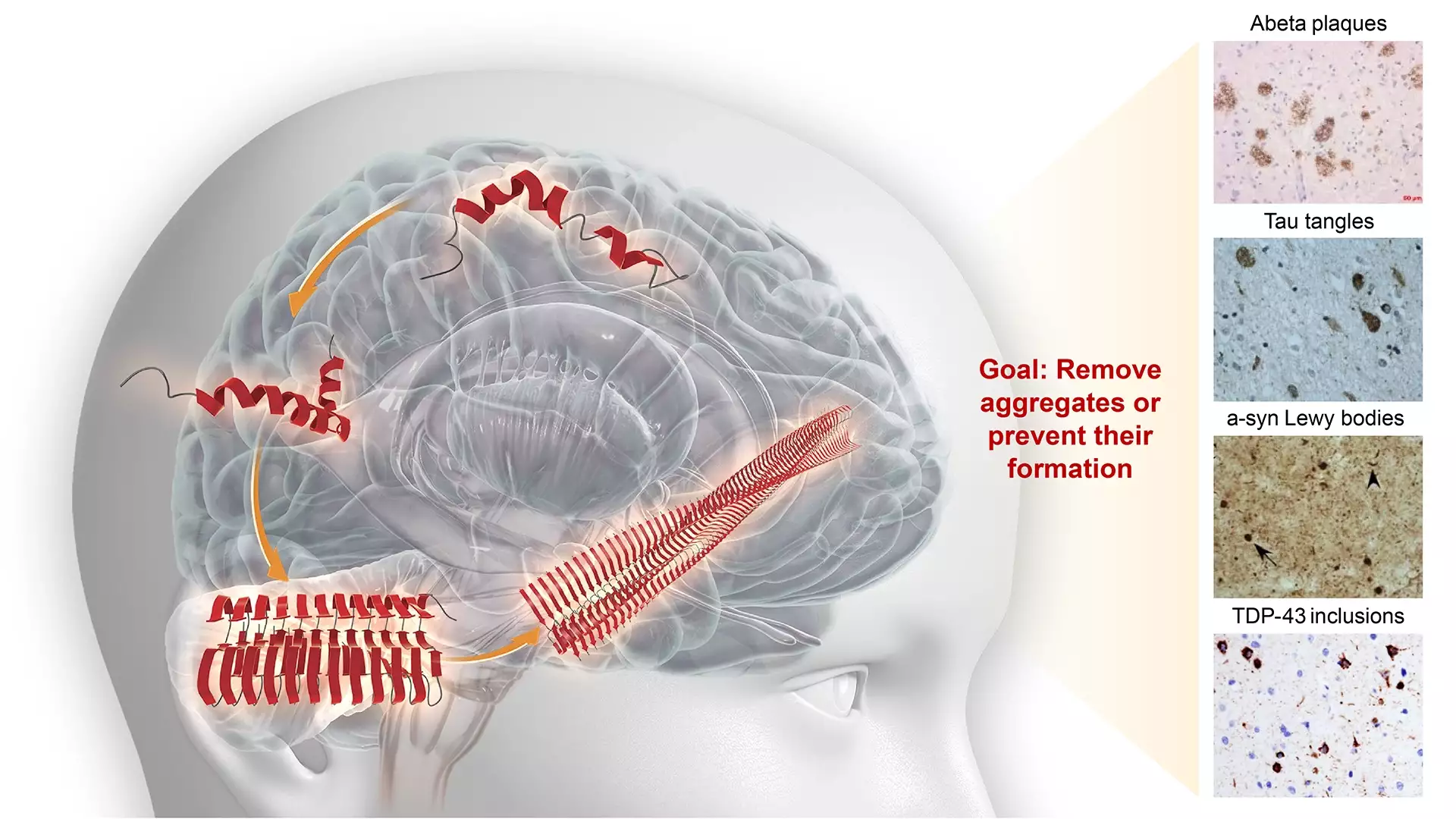
Misfolded proteins – an overarching target
In the healthy brain, normal folding and unfolding of proteins regulate essential biological processes. When incorrect protein folding, or misfolding, occurs, proteins change their shape and become more prone to aggregation and form insoluble deposits within and around neurons.
The progression of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, is closely linked to the spread and aggregation of pathological misfolded proteins throughout the brain. These become toxic to brain cells and damage neurons. Progressively their accumulation can lead to the impairment of function, cognition and, in some diseases, movement.
To successfully treat neurodegenerative diseases, we need technologies to detect misfolded proteins and treatments to prevent aggregation, inhibit spreading and clear aggregates. These treatments would ideally be used at pre-symptomatic stages, because the earlier we intervene, the better our chances of preserving the patient’s function.
Each disease has a specific protein (or set of proteins) that can undergo structural changes and form insoluble aggregates. Addressing this complexity is what motivates AC Immune’s pursuit of precision and combination medicine approaches to target the right protein at the right time.
Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia and may contribute 60–70% of cases, with an estimated global patient population of approximately 55 million people in 2019. This is predicted to increase to 139 million by 2050. The annual global cost of dementia is now above USD 1.3 trillion and expected to rise to US$ 2.8 trillion by 2050.

Alzheimer’s develops because of a complex cascade of events that take place in the brain over a long period of time. Two proteins – Tau and amyloid beta (Abeta) – are recognized as hallmarks of Alzheimer’s. Abnormal species of Tau aggregate into tangles, while plaques and oligomers are formed by Abeta. Both spread throughout the brain and can be found in 70–80% of Alzheimer’s patients. Furthermore, the severity of cognitive impairment correlates with the presence of Tau tangles.
AC Immune is targeting both proteins, Abeta and Tau, with multiple candidates such as monoclonal antibodies (crenezumab and semorinemab, respectively), our Morphomer® Tau small molecule aggregation inhibitor, and active immunotherapies (ACI-24 and ACI-35 programs, respectively) and is advancing a Tau-Positron Emission Tomography (PET) tracer.
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease with over 6 million people living with Parkinson’s disease worldwide. It affects predominantly dopamine-producing neurons and leads to movement-related (“motor”) symptoms but can also result in symptoms that are unrelated to movement (“non-motor”). Progression of the disease tends to be slow and variable: prominent symptoms include tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement. Patients have gait and balance problems, trouble walking and talking, but can also show mental and behavioural changes, sleep problems, depression, memory difficulties, and fatigue.
Alpha-synuclein (a-syn) misfolding, aggregation and seeding are the molecular basis for the formation of Lewy bodies, the hallmark aggregates in Parkinson’s disease. A-syn is a priority target for development of therapeutics and diagnostics in Parkinson’s, and its accumulation is a common cause of dementia and movement disorders, such as Lewy body dementia, multiple system atrophy, and other a-synucleinopathies. It is estimated that over 10 million people worldwide suffer from these conditions. Currently, there are no specific tests to diagnose or differentiate a-synucleinopathies, and diagnosis is still based on medical history and clinical symptoms.
AC Immune is developing a first-in-class a-syn-PET tracer for reliable and accurate diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and other a-synucleinopathies. Therapeutic, potentially disease-modifying, candidates include our clinically validated anti-a-syn active immunotherapy (ACI-7104) as well as anti-a-syn antibodies and Morphomer® small molecule aggregation inhibitors.

LATE
Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE) is a recently characterized and common neurodegenerative disorder of elderly adults, estimated to affect approximately 20–50% of people over the age of 80.
Patients have cognitive impairment, usually an amnesic dementia comparable to Alzheimer disease, although not driven by Abeta or Tau.

TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) has been identified as the primary protein pathology of LATE. In its physiological state, TDP-43 regulates gene transcription. In TDP-43 proteinopathies, misfolding of the protein leads to insoluble TDP-43 aggregates resulting in cellular dysfunction and eventually, clinical symptoms.
The presence of TDP-43 pathology has also been detected in other neurodegenerative diseases (including Alzheimer’s) in the form of a co-pathology, and is thought to exacerbate the observed clinical symptoms. Precise molecular diagnosis and differentiation of brain deposits at early stages might enable a fundamental change in diagnosis and targeted treatment of TDP-43 proteinopathies.
AC Immune is developing a TDP-43-PET imaging tracer and anti-TDP-43 antibodies.
NeuroOrphan
In the U.S., an orphan disease is defined as a condition affecting fewer than 200,000 people nationwide. In the European Union, a rare disease is a condition with a prevalence below 5 in 10,000 people.
Similarly, NeuroOrphan indications are rare diseases of the neurological system such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), multiple system atrophy (MSA) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), and sub-populations of argyrophilic grain disease and Lewy Body Dementia.
There is a high unmet need for these indications, as for most no effective treatment or reliable diagnostic tests are available. Tau and alpha-synuclein have been identified as contributing to several of these NeuroOrphan diseases. TDP-43 is a recently identified target of growing interest for FTLD and ALS.
We believe that our precision medicine approach can be expanded into NeuroOrphan indications. Our first-in-class imaging tracers are well positioned to allow reliable differentiation between conditions that often have overlapping clinical symptoms. Several therapeutic candidates from our broad portfolio could be used to address the identified target.
Our Tau-PET tracer PI-2620 is tested in PSP and CBD for its ability to bind 4-repeat (4R) Tau isoforms, while the first-in-class PET tracers for a-syn and TDP-43 could become the first diagnostics to reliably diagnose MSA or ALS.
From our therapeutics portfolio, AC Immune’s Tau Morphomer® small molecule aggregation inhibitor program is evaluated in rare human Tauopathies. We are also advancing our TDP-43-targeting therapeutics in specific NeuroOrphan indications.

Neuro-
inflammation
In the brain, microglial cells maintain a healthy environment by removing damaged cells and misfolded protein aggregates. When overstimulated in a diseased brain, microglia can drive neurological inflammation and accelerate disease progression.

A key molecular pathway activated in neurodegenerative and other diseases, is the NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor protein 3) inflammasome pathway and a critical component of this pathway is ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain). It is formed and released by activated microglia, and activation of the NLRP3-ASC inflammasome pathway has been shown to exacerbate neuronal damage and promote further neurodegeneration.
ASC specks can be detected in the central nervous system (CNS) of patients with neurodegenerative diseases and pathological species of Abeta, Tau, a-syn and TDP-43 induce NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ASC speck formation. Because of the broad role of this pathway across a number of diseases, NLRP3 and ASC have emerged as attractive and highly valued molecular targets to modulate certain pathological inflammatory responses.
AC Immune is developing multiple small molecule and antibody-based candidates with the potential to inhibit the NLRP3 pathway in CNS and non-CNS indications.

Pioneering Precision Medicine
AC Immune develops the tools to enable detection and clearance of pathological proteins underlying neurodegenerative diseases. Identifying and targeting these misfolded proteins and related pathways in each patient will be key to achieving best possible efficacy.